- December 15, 2023
- Posted by: Netrika
- Category: Uncategorized

What Is Web Penetration Testing
A penetration test, also known as a pen test, is a simulated cyber attack against your computer system to check for exploitable vulnerabilities. In the context of web application security, penetration testing is commonly used to augment a web application firewall (WAF).
A penetration test, also known as a pen test, is a simulated cyber attack against your computer system to check for exploitable vulnerabilities. In the context of web application security, penetration testing is commonly used to augment a web application firewall (WAF).Web penetration testing is a crucial part of a robust cybersecurity strategy that evaluates the security of web applications. Web application security testing incorporates real-world attack simulation strategies to identify vulnerabilities in a web application’s security structure that can potentially be exploited by fraudsters.
Web penetration testing is carried out to understand the current state of an organisation’s web application security, strengthen its defences and protect the sensitive information it carries from cyber attacks.
Penetration testing, a crucial component of cybersecurity, follows a systematic approach to assess the security posture of an organization’s systems and infrastructure.
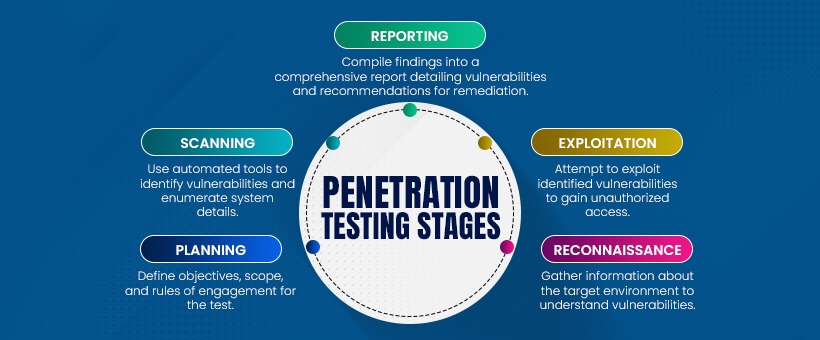
5 Penetration Testing Stages
-
Planning: This initial phase sets the foundation for the entire penetration testing process. It involves defining the objectives, scope, and rules of engagement. Objectives could range from identifying vulnerabilities in specific systems to assessing overall security readiness. Establishing the scope clarifies which systems, networks, or applications will be tested and any limitations or constraints. Rules of engagement outline permissible actions, such as the extent to which testers can simulate attacks without causing disruption. Planning ensures alignment with organizational goals, regulatory requirements, and ethical considerations.
-
Reconnaissance: Also known as information gathering, this stage involves collecting intelligence about the target environment. Testers use various techniques, including passive reconnaissance (examining publicly available information) and active reconnaissance (conducting network scans), to identify potential vulnerabilities and attack vectors. By understanding the organization’s infrastructure, network topology, and system configurations, testers can prioritize areas for further examination.
-
Scanning: In this phase, automated tools are deployed to probe the target systems for vulnerabilities. Vulnerability scanners assess the security posture by identifying weaknesses in software, misconfigurations, or outdated patches. Additionally, network scans reveal open ports, services, and potential entry points for attackers. Scanning provides a comprehensive view of the attack surface, enabling testers to focus their efforts on exploitable vulnerabilities.
-
Exploitation: Building upon the insights gained from reconnaissance and scanning, testers attempt to exploit identified vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access. This phase simulates real-world cyberattacks, such as leveraging known exploits, bypassing authentication mechanisms, or executing malicious code. Successful exploitation demonstrates the potential impact of security weaknesses and highlights areas requiring immediate attention. Testers may escalate privileges to assess the extent of damage an attacker could inflict.
-
Reporting: The final stage involves documenting findings and recommendations in a comprehensive report. The report typically includes an executive summary for stakeholders, detailed technical analysis of vulnerabilities discovered, their severity ratings, and prioritized remediation steps. By providing actionable insights, the report empowers organizations to address weaknesses, enhance defenses, and bolster their overall security posture.
Why is Web Penetration Testing Important?
Web penetration testing allows the simulation of attacks either internally or externally on the system to help businesses understand-
- Mould security posture with the evolving cybersecurity landscape- As the technology is advancing, the cyberattack landscape continues to evolve with more sophistication and cutting-edge tools that can penetrate systems and hit them when they offer the most advantage. Web penetration testing also simulates technologically advanced attacks to identify such vulnerabilities from both internal and external sources to keep an organisation’s defences up-to-date.
- Prevent data breaches from crippling business systems- With devastating legal, financial and reputational consequences of data breaches being a highlight among cybersecurity professionals, web application security testing can both identify and rectify such vulnerabilities proactively before malicious actors exploit them.
- Satisfy regulatory compliance and security policies- Maintaining a security posture is also a part of regulatory compliance. Website penetration testing enables organisations to meet these compliance requirements while helping them mitigate risks before they attack the systems.
- Assess the existing infrastructure- An organisation deploys various infrastructures such as firewalls, and DNS servers to maintain their security posture. However, any changes, upgrades or updates to these infrastructures can make a system prone to cyberattacks. Web penetration testing also identifies such vulnerabilities during simulation.
- Preserve reputation for better user trust- When an organisation’s security is intact, it gains a higher reputation wins its customer trust boosts loyalty and brings more business.
Key Vulnerabilities to watch for, when implementing web application security testing
- SQL Injection
- Cross-Site Scripting
- Authentication and Session Management Issues
- Cross-Site Request Forgery
- File Upload Vulnerabilities
- Insecure Direct Object Reference
- Broken Authentication
- XML External Entity Injection
- Security Misconfigurations
- Server-Side Request Forgery
In today’s world, where cyber attacks are more sophisticated and targeted, website penetration testing is no longer an option but a necessity. It doesn’t just strengthen the web applications but also keeps them resilient against the evolving cyber threats. Moreover, having a robust web penetration testing strategy in place demonstrates your organisation’s commitment to regulatory compliance, data security, and customer trust which is the core for any business’s ethical growth in terms of scale, finances and reputation.
FAQ - Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What Is Web Application Penetration Testing
Web application penetration testing is the practice of simulating attacks on a system in an attempt to gain access to sensitive data, with the purpose of determining whether a system is secure.
Q2. What is penetration testing for example?
A penetration test involves a team of security professionals who actively attempt to break into your company’s network by exploiting weaknesses and vulnerabilities in your systems. Penetration tests may include any of the following methods: Using social engineering techniques to access systems and related databases.
Q3. What is penetration testing in cyber security?
Penetration testing in cybersecurity involves simulated attacks on computer systems and networks to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses, helping organizations strengthen their security defenses and mitigate potential risks.
Q4. What is the purpose of a pen test?
The purpose of a pen test, conducted by Netrika Consulting, is to identify vulnerabilities in computer systems and networks through simulated attacks, helping to strengthen cybersecurity defenses and mitigate potential risks.
Q5. What are the 5 stages of penetration testing?
5 stages in penetration testing:
- Planning and reconnaissance,
- Scanning,
- Gaining access,
- Maintaining access,
- Analysis and reporting.
